ISO 27001 certification is an international standard that defines how organizations should manage and protect sensitive information. It requires the implementation of an Information Security Management System (ISMS) to identify security risks, apply appropriate controls, and ensure continuous improvement in information security. ISO 27001 helps organizations prevent data breaches, protect critical data, and build trust with customers and stakeholders.
What is ISO 27001 certification?
ISO 27001 certification confirms that an organization meets the requirements of the ISO/IEC 27001 standard. It shows that a third-party certification body has reviewed and approved the organization’s information security practices.
In simple terms, ISO 27001 certification proves that:
- Information security risks are properly managed
- Security controls are implemented and monitored
- The organization follows global best practices for data protection
What is the ISO 27001 standard?
The ISO 27001 standard is a globally accepted framework that defines how to build and maintain an Information Security Management System (ISMS). It provides clear requirements for managing information security in a structured way.
The standard follows a risk-based approach, meaning:
- Information security risks are identified
- Risks are analyzed and evaluated
- Appropriate security controls are selected to reduce those risks
ISO 27001 applies to all types of information, including digital data, paper records, and verbal information.
What is an ISMS (Information Security Management System)?
An Information Security Management System (ISMS) is the system used to manage information security on a daily basis. It is the core working model behind ISO 27001 certification.
An ISMS helps organizations:
- Define information security policies and objectives
- Identify and treat security risks
- Apply and monitor security controls
- Assign roles and responsibilities
- Review performance and improve security over time
Example: How ISO 27001 Works in a Real Organization
A growing technology company handled customer data and internal business information. The organization faced common security risks such as unauthorized access, data loss, and lack of clear security policies.
To manage these risks, the company implemented an Information Security Management System (ISMS) based on the ISO 27001 standard. It identified important information assets, performed a risk assessment, and selected appropriate security controls such as access control, password management, and regular data backups.
The organization also documented its security policies, trained employees, and conducted an internal audit. After completing these steps, the company successfully passed the ISO 27001 certification audit conducted by an independent certification body.
As a result, information security improved, security risks were reduced, and customer trust increased. The organization also gained better control over its internal processes and data protection practices.
ISO 27001 clauses explained (Clause 4 to 10)
ISO 27001 requirements are defined in Clauses 4 to 10. These clauses explain how an organization should plan, implement, monitor, and improve its Information Security Management System (ISMS).
Clause 4 – Context of the Organization
This clause focuses on understanding the organization and its environment. It requires identifying internal and external issues, interested parties, and the scope of the ISMS.
Clause 5 – Leadership
Clause 5 highlights the role of top management. Leaders must demonstrate commitment to information security, define roles and responsibilities, and approve the information security policy.
Clause 6 – Planning
This clause deals with planning the ISMS. It includes identifying information security risks, setting security objectives, and planning actions to address risks and opportunities.
Clause 7 – Support
Clause 7 ensures that the ISMS is properly supported. It covers resources, employee competence, awareness, communication, and documentation needed to maintain information security.
Clause 8 – Operation
This clause focuses on the day-to-day operation of the ISMS. It requires implementing security controls, managing risks, and ensuring that information security processes work as planned.
Clause 9 – Performance Evaluation
Clause 9 is about checking how well the ISMS is performing. It includes monitoring and measurement, internal audits, and management reviews to ensure effectiveness.
Clause 10 – Improvement
The final clause focuses on continual improvement. Organizations must address nonconformities, take corrective actions, and continuously improve their information security practices.
| ISO 27001 Clause | Purpose |
| Clause 4 | Organization ka context samajhna |
| Clause 5 | Leadership aur information security policy |
| Clause 6 | Planning aur risk management |
| Clause 7 | Support, resources aur documentation |
| Clause 8 | ISMS operations ka control |
| Clause 9 | Performance evaluation aur internal audit |
| Clause 10 | Continual improvement aur corrective actions |
Annex A controls in ISO 27001
Annex A is an important part of the ISO 27001 standard. It provides a reference list of information security controls that organizations can select based on their identified risks. These controls help reduce security threats and protect information assets.
Annex A controls are grouped into key security areas, including:
- Access control – Ensures only authorized users can access information
- Asset management – Identifies and protects information assets
- Cryptography – Protects data through encryption techniques
- Physical and environmental security – Secures offices, data centers, and equipment
- Operations security – Maintains secure day-to-day operations
- Communications security – Protects data shared across networks
- Supplier relationships – Manages security risks from third-party vendors
- Incident management – Detects, reports, and responds to security incidents
Organizations choose the controls that apply to their risks and document them in the Statement of Applicability (SoA). The SoA explains which controls are implemented, which are excluded, and the reasons behind each decision.
Why is ISO 27001 certification important?
ISO 27001 certification is important because organizations face growing risks related to data breaches, cyber threats, and information misuse. It provides a structured approach to identify security risks and apply controls to protect sensitive information.
Key benefits of ISO 27001 certification include:
- Strong protection of sensitive data by managing security risks effectively
- Reduced risk of cyber attacks and data breaches through defined security controls
- Increased trust from customers, partners, and stakeholders
- Improved internal processes and employee security awareness
- Support for legal, regulatory, and contractual information security requirements
Who needs ISO 27001 certification?
ISO 27001 certification is suitable for organizations of all sizes that handle sensitive or confidential information. It is especially important for businesses that manage customer data, financial records, or critical systems.
ISO 27001 certification is commonly required by:
- IT and software companies handling client or application data
- SaaS and cloud service providers managing user information
- Startups that store or process customer data
- Healthcare and financial organizations dealing with sensitive records
- Enterprises managing large volumes of business and customer information
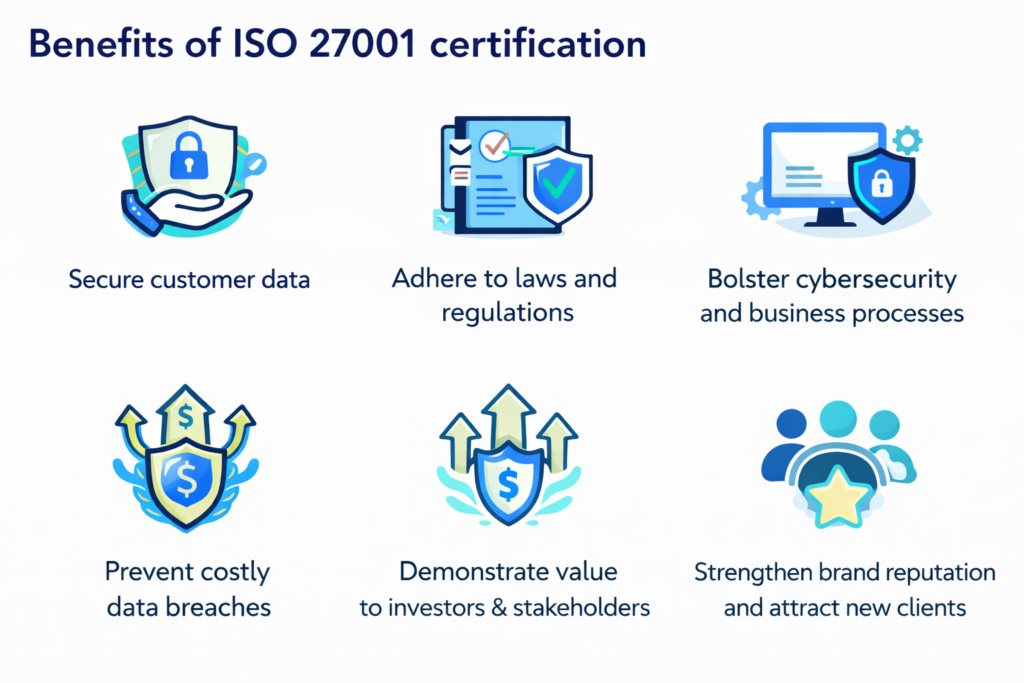
ISO 27001 Certification Process (Step-by-Step)
The ISO 27001 certification process follows a systematic approach to help organizations identify information security risks, implement controls, and achieve certification.
Step 1: Gap Analysis: The organization reviews its existing information security practices and compares them with ISO 27001 requirements to identify gaps that need to be addressed.
Step 2: Risk Assessment: Information assets are identified, potential security risks are analyzed, and the impact of those risks is evaluated.
Step 3: Risk Treatment: Based on the risk assessment, appropriate information security controls are selected to reduce, avoid, or manage identified risks.
Step 4: Documentation: Required ISO 27001 documents, such as policies, procedures, and records, are prepared and approved to support the ISMS.
Step 5: ISMS Implementation: The Information Security Management System (ISMS) is implemented across the organization, and security controls are put into operation.
Step 6: Internal Audit: An internal audit is conducted to verify that the ISMS is effectively implemented and compliant with ISO 27001 requirements.
Step 7: Certification Audit
An independent certification body performs the final audit in two stages
- Stage 1 Audit – Review of ISMS documentation and readiness
- Stage 2 Audit – Assessment of ISMS implementation and effectiveness
Successful completion of the certification audit results in ISO 27001 certification.
ISO 27001 certification lifecycle
ISO 27001 certification follows a three-year lifecycle to ensure that information security controls remain effective over time.
- Year 1 – Certification Audit and Approval: The organization completes the Stage 1 and Stage 2 audits. If all requirements are met, ISO 27001 certification is granted.
- Year 2 – Surveillance Audit: A surveillance audit is conducted to confirm that the ISMS is being maintained and continues to comply with ISO 27001 requirements.
- Year 3 – Surveillance Audit and Recertification: Another surveillance audit is performed, followed by a recertification audit to renew the ISO 27001 certificate for the next cycle.
Regular audits help organizations monitor performance, address gaps, and continuously improve their information security management system.
Simple risk assessment example
A basic ISO 27001 risk assessment follows a clear and practical structure. The goal is to identify what needs protection, understand the risk, and apply the right control.
- Asset – Customer database
- Risk – Unauthorized access to the data
- Impact – Data breach, loss of customer trust, and possible legal issues
- Control – Access control, strong authentication, and regular monitoring
This approach helps organizations focus on real risks and select appropriate security controls instead of applying unnecessary measures.
ISO 27001 documentation overview
ISO 27001 requires clear and well-maintained documentation to support the Information Security Management System (ISMS). These documents show how information security risks are identified, controlled, and reviewed.
Key documents required for ISO 27001 certification include:
- Information Security Policy – Defines the organization’s approach to information security
- Risk Assessment and Risk Treatment Plan – Identifies risks and explains how they are managed
- Statement of Applicability (SoA) – Lists selected Annex A controls and justifies their use
- Asset Inventory – Records important information assets and ownership
- Internal Audit Report – Confirms ISMS effectiveness and compliance
- Management Review Records – Shows leadership involvement and decision-making
Documentation should be practical, up to date, and aligned with actual business processes, not created only for audit purposes.
ISO 27001 certification vs compliance
ISO 27001 compliance means following the standard internally, while ISO 27001 certification means that an independent certification body has verified and approved the Information Security Management System (ISMS).
| ISO 27001 Certification | ISO 27001 Compliance |
| Involves a third-party audit | Implemented internally within the organization |
| ISMS is verified by an accredited certification body | No external verification is performed |
| An official ISO 27001 certificate is issued | No certificate is issued |
| Builds higher trust with clients and partners | Provides limited external assurance |
| Often required for contracts and tenders | Mainly used for internal security improvement |
Common mistakes during ISO 27001 certification
Many organizations face delays or audit failures because of common mistakes made during ISO 27001 implementation.
Common mistakes include:
- Using copy-paste documentation without performing a proper risk assessment
- Weak or incomplete internal audits before the certification audit
- Lack of employee awareness and training on information security practices
- Treating ISO 27001 as a one-time activity instead of a continuous process
Avoiding these mistakes helps organizations achieve certification smoothly and maintain an effective ISMS over time.
ISO 27001 Certification Services
ISO 27001 certification services help organizations implement and maintain an effective Information Security Management System (ISMS) and achieve certification smoothly. These services reduce complexity, save time, and lower the risk of audit nonconformities.
ISO 27001 certification services typically include:
- Gap analysis and readiness assessment to identify areas that need improvement
- Risk assessment guidance to identify and manage information security risks
- Documentation development aligned with ISO 27001 requirements
- Internal audit support to verify ISMS effectiveness before certification
- Certification audit preparation to ensure audit readiness and successful certification
Professional ISO 27001 certification services help organizations follow the standard correctly and maintain compliance over time.
How JS CERTIFICATION Supports Organizations
JS CERTIFICATION provides ISO 27001 certification services with over 5 years of experience in information security management and ISO standards. The team helps organizations implement an effective Information Security Management System (ISMS) and achieve certification with clarity and confidence.
JS CERTIFICATION supports organizations throughout the entire ISO 27001 journey, including documentation development, risk assessment, internal audits, and certification readiness, ensuring full alignment with ISO/IEC 27001 requirements.
Ready to start your ISO 27001 journey?
If you are planning to get ISO 27001 certified or want to assess your current readiness, expert guidance can save time and reduce audit risks.
- Get a free initial consultation
- Request an ISO 27001 audit readiness check
- Get clear guidance on process, documentation, and certification steps
👉 Contact JS CERTIFICATION today to move toward ISO 27001 certification with confidence.
Conclusion
ISO 27001 certification helps organizations protect sensitive information, manage security risks, and build long-term trust with customers and partners. By implementing the ISO 27001 standard and maintaining a strong Information Security Management System (ISMS), businesses can improve data security, meet global information security expectations, and demonstrate a clear commitment to information protection.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is ISO 27001 certification and why is it important?
ISO 27001 certification is an international standard that confirms an organization has implemented an effective Information Security Management System (ISMS). It is important because it helps businesses protect sensitive information, reduce security risks, prevent data breaches, and build trust with customers, partners, and stakeholders.
2. Who should get ISO 27001 certification?
ISO 27001 certification is recommended for organizations that handle sensitive data, such as customer information, financial records, or confidential business data. It is commonly required for IT companies, SaaS providers, startups, healthcare organizations, financial institutions, and enterprises that need strong information security controls.
3. How long does ISO 27001 certification take?
The time required for ISO 27001 certification depends on the size of the organization and the scope of the ISMS. In most cases, the certification process takes 3 to 6 months, including documentation, implementation, internal audits, and the certification audit.
4. Is ISO 27001 certification mandatory?
ISO 27001 certification is not legally mandatory, but many clients, partners, and contracts require it as proof of information security practices. Organizations often choose ISO 27001 certification to meet customer expectations, regulatory requirements, and international business standards.
5. What is the difference between ISO 27001 certification and compliance?
ISO 27001 compliance means following the standard internally, while ISO 27001 certification means an independent certification body has audited and approved the organization’s ISMS. Certification provides official recognition and higher external trust compared to internal compliance alone.